SciLake at the INORMS Congress 2025
SciLake at the INORMS Congress 2025
At the INORMS Congress 2025 in Madrid, SciLake partners from OpenAIRE showcased and promoted open and federated infrastructures as essential tools for transparent, inclusive, and sustainable research assessment. The event provided an excellent opportunity to engage with the global research management community and expand Open Science practices among research managers and administrators.

SciLake partners from OpenAIRE recently presented their work on open and federated infrastructures at the INORMS Congress 2025 in Madrid. The presentation, titled "A Scientific Lake to Democratise Knowledge: The OpenAIRE Graph and SciLake's Ecosystem" was delivered by Giulia Malaguarnera from OpenAIRE, in collaboration with Stefania Amodeo (OpenAIRE) and Thanasis Vergoulis (Athena RC).
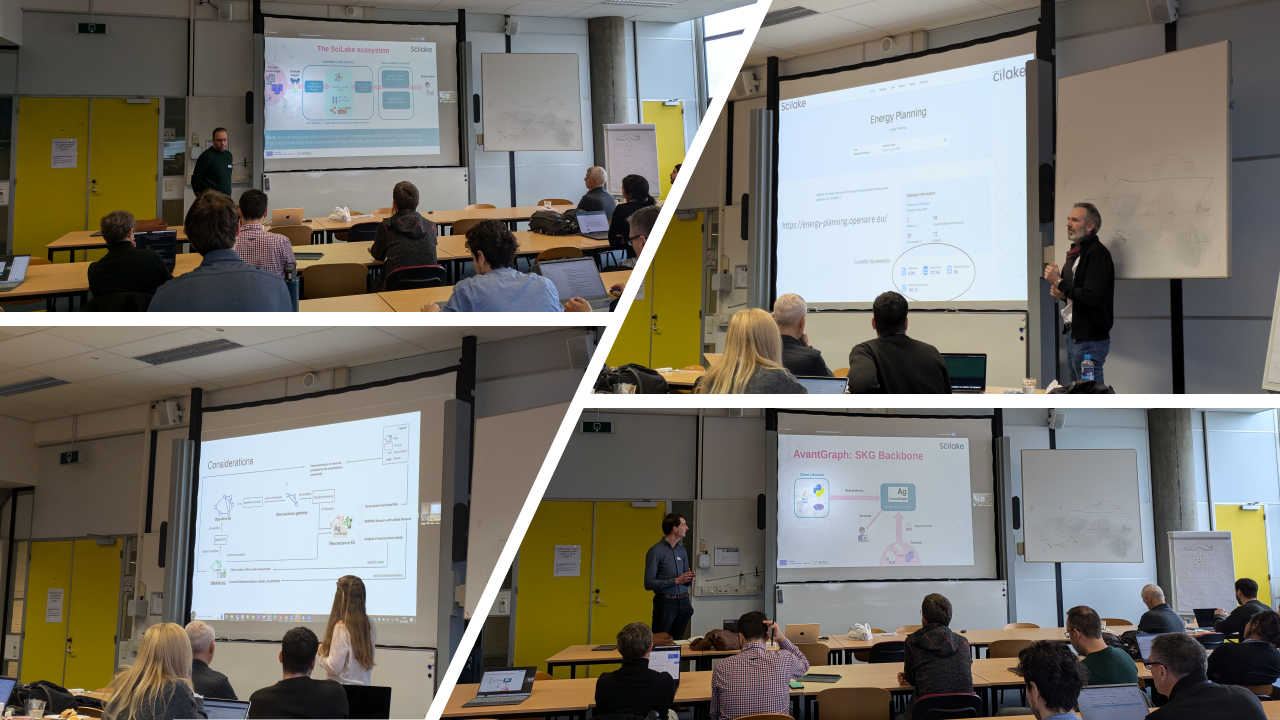
At the heart of SciLake's innovation is its "Scientific Lake" concept: a comprehensive ecosystem of customizable components that enables researchers to create, interlink, and maintain domain-specific Scientific Knowledge Graphs (SKGs). This ecosystem significantly enhances research capabilities by providing seamless access to scientific data and offering discipline-specific services.
The project builds upon the OpenAIRE Graph, a global SKG containing over 250M research outputs from more than 130,000 sources. This extensive database links publications, data, and software with their funding sources and creators, while tracking their impact.
The presentation showcased the SciLake ecosystem of components, demonstrating how our innovative approach combines the power of the OpenAIRE Graph with domain-specific knowledge to create a versatile and user-friendly system that is used by researchers across diverse fields.
How Does SciLake Empower Research Management?
For research administrators, SciLake offers practical benefits by streamlining workflows through centralized data access and automated analysis tools. The SciLake toolkit ensures transparent evaluation processes and provides constant data updates, significantly reducing manual effort in report generation.
Find the presentation on Zenodo